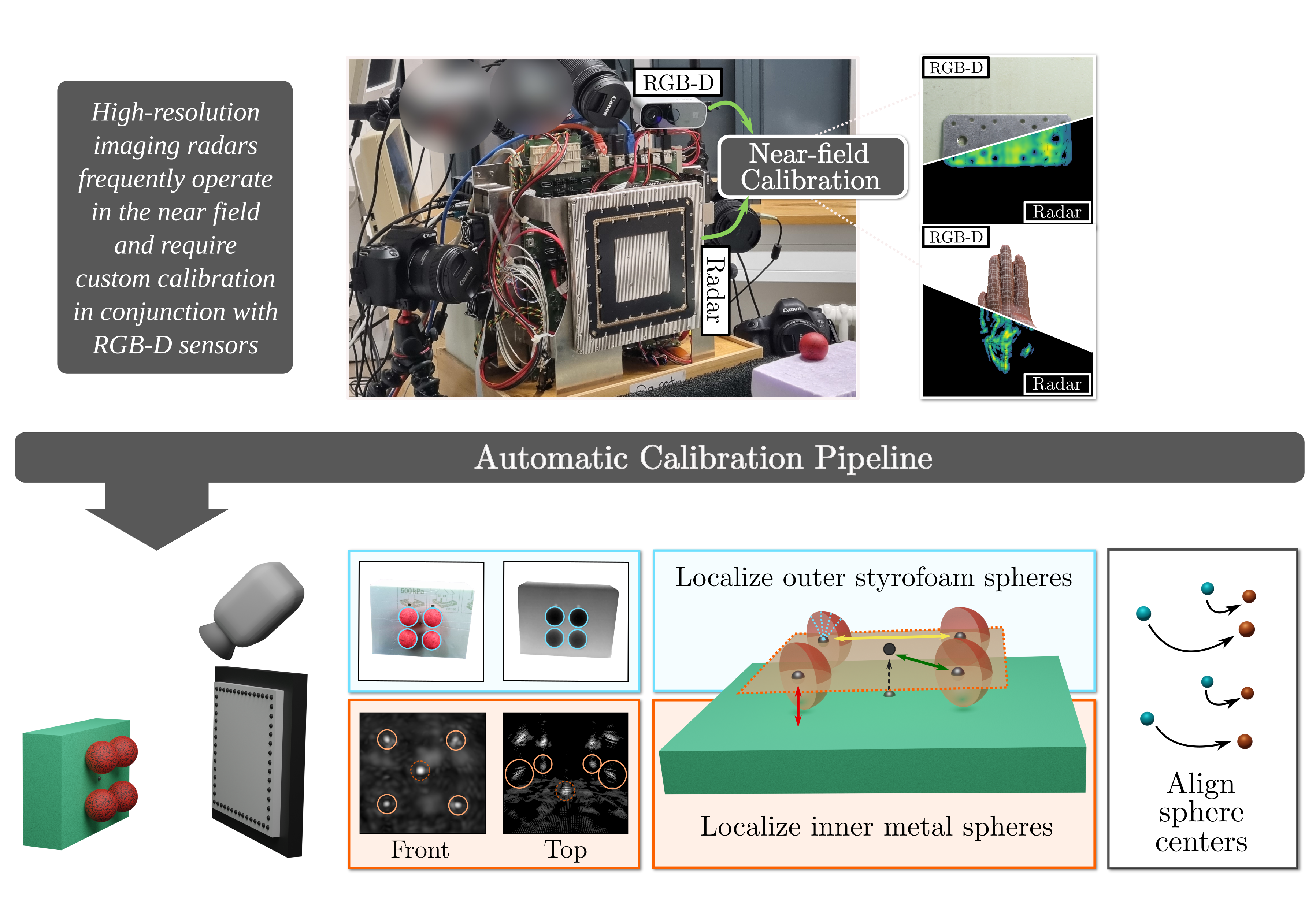
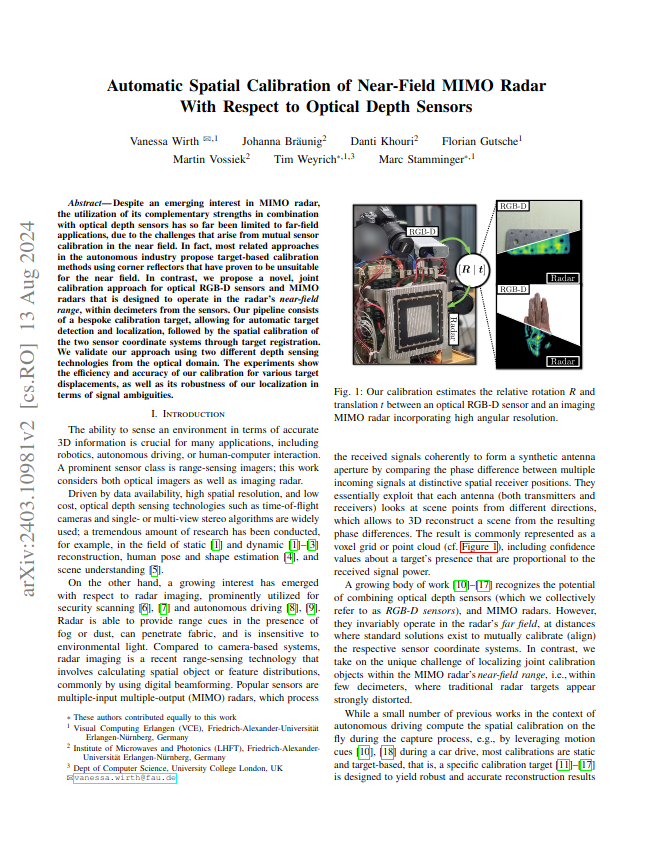
Despite an emerging interest in MIMO radar, the utilization of its complementary strengths
in combination with optical depth sensors has so far been limited to far-field applications,
due to the challenges that arise from mutual sensor calibration in the near field. In fact,
most related approaches in the autonomous industry propose target-based calibration methods
using corner reflectors that have proven to be unsuitable for the near field.
In contrast, we propose a novel, joint calibration approach for optical RGB-D sensors and
MIMO radars that is designed to operate in the radar's near-field range, within decimeters
from the sensors. Our pipeline consists of a bespoke calibration target, allowing for
automatic target detection and localization, followed by the spatial calibration of the two
sensor coordinate systems through target registration.
We validate our approach using two different depth sensing technologies from the optical
domain. The experiments show the efficiency and accuracy of our calibration for various
target displacements, as well as its robustness of our localization in terms of signal
ambiguities.